Top Intraoral Scanners Manufacturers Comprehensive Guide Sourcing from China.
Top Intraoral Scanners in China introduce
China has a burgeoning market for intraoral scanners, driven by advancements in dental technology and a growing focus on digital dentistry. Here are the top intraoral scanners currently popular in China:
Here is the updated comparison table including the intraoral products from Shanghai Carejoy Medical:
| Company | Product | Description | Image | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medit | Medit i700 Wireless | Premium intraoral scanner for digital dentistry. |  | Medit |
| Launca | DL-300 Wireless | Wireless scanning, high accuracy, fast scanning speeds. |  | Launca |
| Panda Scanner | PANDA P4 | High-tech digital intraoral scanner, accurate and clear shoulder margin, high-definition color images. |  | Panda Scanner |
| BLZ Dental | INO200 Intraoral | Easy to operate, quickly obtain reliable and accurate 3D digital impression, enhances communication between dentist and patient. |  | BLZ Dental |
| Carejoy | Intraoral Scanner | Accurate, high-definition 3D digital impressions, dynamic real-time 3D imaging, LED light source, USB 3.0 interface, supports .OBJ, .PLY, .STL formats. |  | Carejoy |
Each entry now includes the company name, product name, description, image, and link to the respective website for further details.
These companies offer a broad spectrum of dental scanning solutions, characterized by precision, ease of use, and integration with CAD/CAM systems, catering to China’s evolving dental practice needs.
Types of Intraoral Scanners
Intraoral scanners (IOS) are digital devices used in dentistry to create precise 3D images of the inside of a patient’s mouth. These images assist in various dental procedures, including creating crowns, bridges, and orthodontic appliances. The main types of intraoral scanners are:
1. Triangulation-Based Scanners:
These scanners use the principle of triangulation, where a light source emits a beam that reflects off the tooth and is captured by sensors. The difference in angles of the emitted and reflected beams creates a 3D image. Examples include early versions of CEREC by Dentsply Sirona.
2. Confocal Microscopy Scanners:
These emit light at specific wavelengths and measure the reflected light to create detailed images. Confocal microscopy can offer increased depth and accuracy. A key example is the 3Shape TRIOS, known for its high accuracy and color scanning capabilities.
3. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Scanners:
Using a similar principle to ultrasound but with light, OCT scanners provide highly detailed 3D images by measuring the reflection of light waves. Examples include the iTero system, which is widely used for Invisalign treatments.
4. Active Wavefront Sampling:
This technology uses wavefront sampling to produce accurate 3D images and is relatively quick. Examples include the Carestream CS series, which offers user-friendly interfaces and high-speed scanning.
5. Multispectral Imaging:
This type uses multiple wavelengths of light to capture a broader range of data, improving color accuracy and surface detail. An example is the Planmeca Emerald scanner, which is compact and offers high-resolution images.
Each type of IOS has its advantages and specific use cases, with continuous advancements making them increasingly accurate, faster, and more user-friendly.
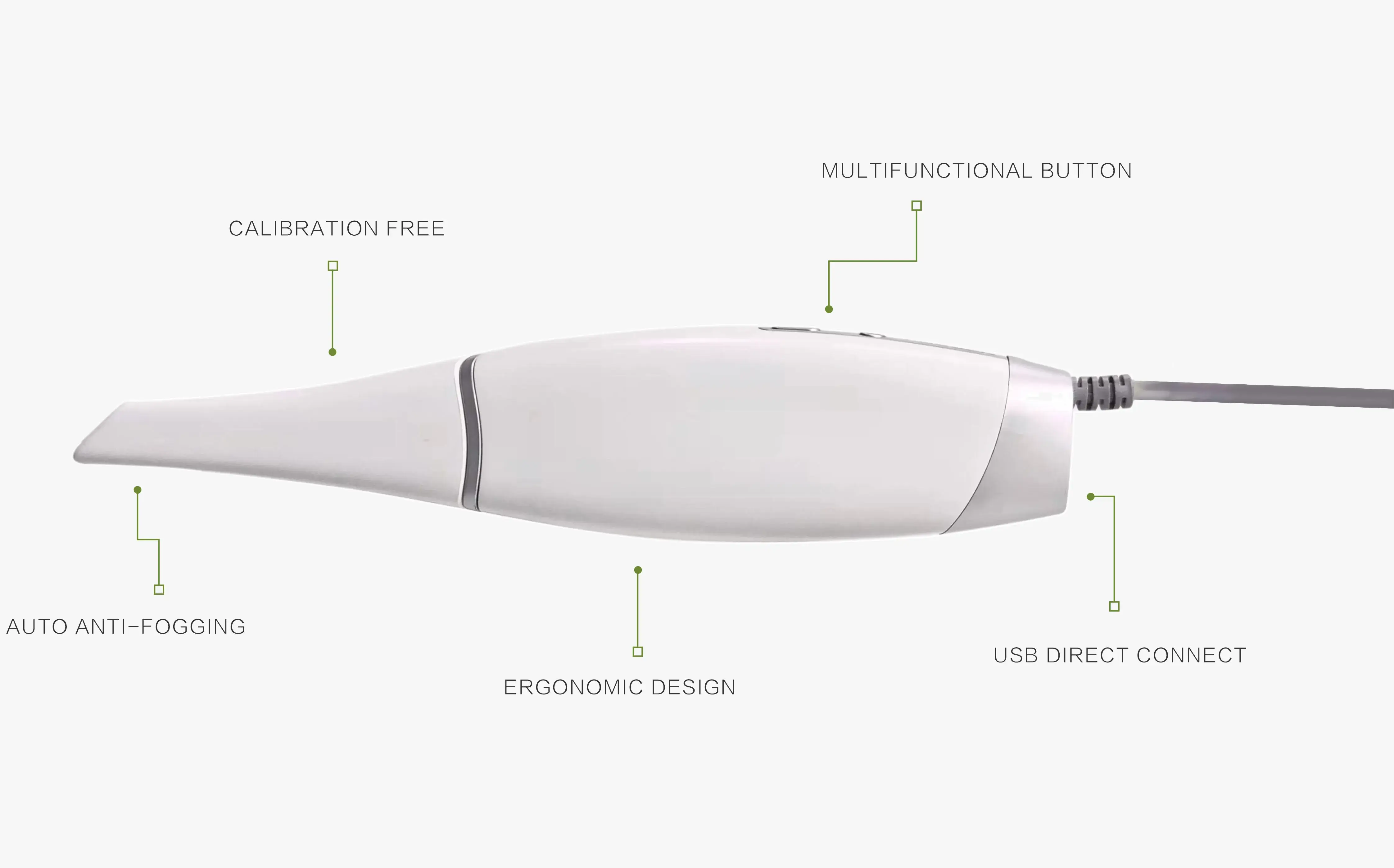
Pros and Cons of Using Intraoral Scanners
Pros and Cons of Using Intraoral Scanners
Pros:
1. Accuracy and Precision: Intraoral scanners provide highly accurate and precise digital impressions, reducing the risk of human error and improving the quality of dental restorations.
2. Patient Comfort: Unlike traditional methods that require uncomfortable impression materials, intraoral scanners are non-invasive, making the procedure more pleasant for patients.
3. Speed: Scanning takes significantly less time than traditional impression techniques, allowing for quicker appointments and faster turnaround for restorative work.
4. Digital Workflow Integration: Intraoral scanners seamlessly integrate with other digital dental technologies, such as CAD/CAM systems, streamlining the workflow from diagnosis to treatment planning to prosthesis fabrication.
5. Enhanced Communication: The digital images captured can be easily shared with patients, specialists, and labs, improving communication and collaboration in treatment planning and execution.
6. Environmentally Friendly: Using digital impressions reduces the need for disposable materials such as impression trays and silicone, contributing to a greener practice.
Cons:
1. Initial Cost: The upfront investment in intraoral scanner technology can be high, which may be a barrier for smaller or budget-conscious practices.
2. Learning Curve: Dental professionals may need time and training to become proficient in using intraoral scanners and integrating them into their practice effectively.
3. Maintenance and Updates: Ongoing maintenance and software updates are required to keep the technology running smoothly, potentially adding to the cost and operational complexities.
4. Compatibility Issues: Not all intraoral scanners are compatible with every digital system or software, which may cause integration challenges within existing workflows.
5. Dependence on Technology: Relying heavily on digital technology could lead to disruptions if technical issues arise, such as software glitches or scanner malfunctions.
In summary, intraoral scanners offer significant advantages in terms of accuracy, patient comfort, and workflow efficiency, but they also come with substantial costs and technical demands that must be carefully considered.
Intraoral Scanners Reference Specifications (varies for different product)
Intraoral scanners (IOS) have revolutionized dental practices by enabling precise and quick digital impressions. Various brands and models offer unique features, but several key specifications are commonly considered when comparing these devices:
1. Accuracy: Generally, the accuracy of intraoral scanners should be within the range of 10 microns for optimal results. This ensures a true-to-life digital representation of the patient’s dental structure.
2. Scanning Speed: Speed is critical for patient comfort and efficiency in practice. The scanning time can vary from 2-5 minutes for a full arch, depending on the device and operator’s experience.
3. Field of View (FOV): A larger FOV allows more data to be captured per scan, which can range from approximately 14×14 mm to 22×22 mm, facilitating quicker scans.
4. Imaging Technology: Most modern scanners use confocal microscopy, triangulation, or parallel confocal imaging to capture detailed images. The choice of technology impacts accuracy and speed.
5. Ease of Use: Factors like ergonomic design, weight (typically under 400 grams), and intuitive software interfaces are crucial for user comfort and efficiency.
6. Compatibility: Integration with computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software is essential for streamlined workflows. Open architecture systems offer more flexibility in digital workflows.
7. Battery Life: For portable models, battery life can vary but generally should last throughout multiple scanning sessions, typically around 1-2 hours of continuous use.
8. Resolution: High resolution, typically around 15-25 microns, is essential for detailed imagery, improving diagnostics and treatment outcomes.
9. Connectivity: Wireless options offer enhanced mobility but should maintain robust data transfer rates to avoid lag.
10. Sterilization and Hygiene: Removable, autoclavable scanner tips are standard for maintaining hygiene and preventing cross-contamination.
11. Cost: Prices range widely from $20,000 to $50,000, depending on features, brand, and bundled software/services.
By focusing on these specifications, dental professionals can select the most suitable intraoral scanner for their practice needs.

Applications of Intraoral Scanners
Intraoral scanners (IOS) have revolutionized dental practice by offering digital alternatives to traditional impression methods. These devices capture detailed 3D images of the oral cavity, providing numerous applications across various dental disciplines.
1. Prosthodontics: IOS enhances the fabrication of dental prosthetics, including crowns, bridges, and dentures. The high-precision digital impressions ensure better fit and comfort, reducing the need for multiple adjustments.
2. Orthodontics: Digital impressions streamline the diagnosis and treatment planning for orthodontic cases. Scanners aid in creating accurate models for custom orthodontic appliances such as braces and aligners, facilitating effective treatment and shorter chair time.
3. Implantology: Intraoral scanners play a crucial role in the planning and placement of dental implants. They provide accurate data for computer-guided surgery, improving implant placement precision and reducing surgical risks.
4. Restorative Dentistry: IOS supports the design and fabrication of inlays, onlays, and veneers. The digital workflow enhances the accuracy of these restorations, contributing to superior esthetic and functional outcomes.
5. Oral Surgery: For surgical procedures requiring precision, such as bone grafts or extractions, intraoral scanners offer detailed visualization of the oral anatomy, aiding in enhanced surgical planning and execution.
6. Patient Education: The 3D images generated by IOS help dentists communicate treatment plans more effectively to patients. This visual aid enhances patient understanding and engagement, leading to higher satisfaction and acceptance rates.
7. Digital Record Keeping: Maintaining digital dental records simplifies case documentation and long-term patient monitoring. It also facilitates easy sharing of patient data with specialists or dental labs, improving interdisciplinary collaboration.
8. Research and Development: Intraoral scanners provide valuable data for clinical research and the development of new dental materials and techniques, advancing the field of dentistry.
Overall, intraoral scanners contribute to enhanced diagnostic accuracy, treatment efficiency, and patient comfort, representing a significant advancement in modern dental care.
Material of Intraoral Scanners
Intraoral scanners (IOS) are advanced dental devices used to capture direct oral impressions digitally. These scanners rely on precise optical systems and sophisticated materials to ensure accuracy, durability, and patient comfort. The primary materials involved in the construction of intraoral scanners include:
1. Housing Materials:
– Medical-Grade Plastics: Typically used for the outer casing, these plastics are lightweight, durable, and biocompatible. They can withstand regular sterilization processes and are often designed to be ergonomic for ease of handling by dental professionals.
– Metals: High-quality metals, such as aluminum or stainless steel, are sometimes used for structural components to enhance durability and robustness.
2. Optical Components:
– Glass and Sapphire Lenses: These materials are used for lenses and mirrors because of their high transparency and resistance to scratching and staining. Glass and sapphire ensure the clear transmission of light, which is crucial for accurate 3D imaging.
– CMOS and CCD Sensors: These semiconductor materials are integral to capturing detailed images by converting light into electronic signals. CMOS sensors are particularly valued for their high-speed performance and energy efficiency.
3. Electronic Circuits:
– Silicon-Based Components: The internal circuitry, including processors and memory units, is made from silicon. This material is essential for the fast processing and storage of the captured data.
4. Light Sources:
– LEDs and Lasers: Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and laser diodes are used to project light into the oral cavity, which reflects off the surfaces and is captured by the scanner’s sensors. These light sources must be precise and consistent to ensure high-quality images.
In summary, intraoral scanners are constructed from a combination of medical-grade plastics, metals, advanced optical materials like glass and sapphire, and high-tech electronic components. These materials collectively ensure the scanners are reliable, accurate, and safe for dental use.
Quality Testing Methods for Intraoral Scanners and how to control the quality
Quality testing for intraoral scanners is crucial for ensuring accuracy, reliability, and user satisfaction. These advanced devices capture digital impressions of patients’ oral cavities and have become indispensable in modern dentistry. Here’s a concise overview of key quality testing methods and control strategies:
Testing Methods:
1. Accuracy and Precision Testing:
– Resolution Tests: Use calibration objects with known dimensions to check if the scanner accurately captures fine details.
– Repeatability: Conduct multiple scans of the same object and compare results to assess if the device consistently produces the same output.
2. Field of View (FOV) Assessment:
– Ensure the scanner covers the required area within the oral cavity by testing on standard dental models.
3. Ergonomics and Usability Testing:
– Hands-on Trials: Dentists and hygienists use the scanner in simulated clinical environments to provide feedback on ease of use, weight, and comfort.
4. Software Performance:
– Evaluate the scanning software for intuitiveness, processing speed, and accuracy in data rendering.
5. Durability and Sterility:
– Stress Testing: Simulate long-term use by repeatedly handling, cleaning, and sterilizing the scanner.
– Material Safety: Verify that materials used in the scanner are biocompatible and can withstand repeated sterilization without degrading.
Quality Control Strategies:
1. Standardization:
– Develop standardized procedures for scanner calibration and use, based on established dental industry guidelines.
2. Regular Calibration:
– Implement routine calibration schedules using standard calibration tools and software provided by the manufacturer.
3. User Training:
– Provide comprehensive training for dental professionals to ensure the scanner is used correctly and efficiently.
4. Feedback Mechanisms:
– Establish channels for users to report issues or suggest improvements. Regularly review and address this feedback to enhance product design and functionality.
5. Maintenance Protocols:
– Create detailed maintenance protocols to ensure the scanner remains in optimal condition, including routine checks and timely repairs.
By combining rigorous testing with robust quality control strategies, dental practices can ensure that intraoral scanners deliver reliable, high-quality digital impressions, thereby improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
The Work Process and how to use Intraoral Scanners
Intraoral scanners are advanced digital tools used in dentistry to capture detailed 3D images of patients’ oral structures. Here’s a concise overview of the work process and usage:
1. Preparation: Begin by ensuring the intraoral scanner is clean, calibrated, and ready for use. Inform the patient about the procedure to reduce anxiety.
2. Scanning:
– Initial Setup: Position the patient comfortably and adequately illuminate the oral cavity.
– Start Scanning: Gently insert the scanning wand into the patient’s mouth. Modern scanners are designed for patient comfort and ease of use.
– Scan Technique: Employ a systematic approach, usually starting with the upper arch, then the lower arch, followed by a bite registration. Move the scanner slowly and steadily to capture a series of overlapping images.
– Real-Time Feedback: Most scanners provide real-time visual feedback on the screen, ensuring complete and accurate scans. Pause occasionally to inspect the progress and rescan if necessary.
3. Post-Scanning:
– Review and Edit: Once the scan is complete, review the digital model for any missing or distorted areas. Use the software tools to edit or rescan specific sections if needed.
– Data Management: Save the digital files securely. These files can be used for various dental applications, including creating crowns, bridges, aligners, or other prosthetic devices.
– Communication: Share the digital models with the dental lab or other dental professionals as required, often through cloud-based systems.
4. Disinfection: Follow stringent sterilization protocols to clean the scanning wand and other contact surfaces to maintain hygiene and prevent cross-contamination.
Benefits: Intraoral scanners enhance precision, reduce patient discomfort, cut down chair time, and streamline workflows compared to traditional impression methods.
By integrating intraoral scanners, dental practices can provide more accurate, efficient, and patient-friendly services.
Intraoral Scanners Importing questions including Cost,Supplier,Sample,Certification and Market
Importing intraoral scanners involves a multi-faceted approach considering cost, suppliers, samples, certifications, and market dynamics.
Cost: Intraoral scanners typically range from $15,000 to $50,000, depending on features, brand, and software integration. Additional expenses can include shipping, insurance, tariffs, and maintenance.
Suppliers: Key suppliers include 3Shape, Dentsply Sirona, iTero by Align Technology, Planmeca, and Carestream Dental. It’s crucial to source from reputable suppliers to ensure quality and reliable after-sales support.
Sample: Requesting a sample can help evaluate the scanner’s performance and compatibility with your practice’s needs. Many suppliers offer demonstration units or 30-day trial periods. Ensure the sample represents the final product and inquire about any costs associated with the trial.
Certification: To import and use intraoral scanners, ensure they comply with local regulatory standards. In the U.S., look for FDA approval, while CE marking is essential for the European market. These certifications verify the product meets safety and efficacy standards.
Market: The demand for intraoral scanners is growing due to their efficiency in capturing 3D impressions, improving patient experience, and facilitating digital workflows in dentistry. Understanding market trends, competitor offerings, and patient demographics can guide your purchasing decision. Consider offering training and support to optimize usage and outcomes.
Engaging with industry experts, attending dental trade shows, and reading reviews can provide deeper insights into the best products and practices. Thorough research and strategic planning are indispensable for successfully importing and integrating intraoral scanners into your dental practice.
How to find and select check reliable Intraoral Scanners manufacturers in China
Finding and selecting reliable intraoral scanner manufacturers in China involves careful research and verification. Here’s a streamlined approach:
1. Online Research:
– Directories: Use platforms like Alibaba, Made-in-China, and Global Sources to find manufacturers.
– Company Websites: Visit the manufacturer’s official website for detailed product information, certifications, and company background.
2. Verify Credentials:
– Certifications: Ensure the manufacturer is ISO 13485 certified, indicating they meet regulatory requirements for medical devices.
– Product Approvals: Check for FDA or CE certifications for their products, showcasing compliance with international standards.
3. Customer Reviews and Testimonials:
– Alibaba Reviews: Look at the ratings, reviews, and feedback on Alibaba or other e-commerce platforms.
– Case Studies: Request case studies or testimonials from the manufacturer to understand their market reputation.
4. Manufacturer’s Experience:
– Years in Business: Prefer manufacturers with several years in the industry, indicating stability and experience.
– Clientele: Check if they supply to well-known brands or international clients.
5. Factory Visit:
– Audit: If possible, visit the factory to audit their production process, quality control, and facilities.
– Virtual Tours: In case a visit isn’t feasible, request a virtual tour.
6. Quality Assurance:
– Testing: Inquire about their quality assurance and testing processes.
– Samples: Request product samples to assess the build quality and performance.
7. Communication:
– Responsiveness: Evaluate their communication efficiency and support. Reliable manufacturers usually have responsive customer support.
8. Trade Show Participation:
– Exhibitions: Check if the manufacturer participates in relevant dental or medical device trade shows like the International Dental Show (IDS).
Following these steps will help you identify and select a reliable intraoral scanner manufacturer in China.
Background Research for Intraoral Scanners manufacturers Companies in China, use qcc.com archive.org importyeti.com
Intraoral scanners are devices used primarily in dental practices for capturing detailed 3D images of the inside of a patient’s mouth. China has emerged as a significant player in the production of these devices, driven by technological advancements and growing demand in both domestic and international markets.
Chinese companies involved in the manufacturing of intraoral scanners include several well-established firms. According to qcc.com, a business data platform, prominent names in this sector encompass Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd, Foshan Core Deep Medical Apparatus Co., Ltd, and Shining 3D Tech Co., Ltd. These companies are notable for their extensive research and development capabilities as well as competitive pricing strategies that make them formidable competitors globally.
Shining 3D Tech Co., Ltd, for example, is renowned for integrating 3D digitizing technologies across various applications, including dental imaging. Archive.org data reflect the company’s ongoing efforts to improve image accuracy and user experience through innovation.
ImportYeti.com, which provides insights into a company’s supply chain activities, shows that Mindray Bio-Medical has been actively exporting dental equipment to numerous countries. Their intraoral scanners are among the products that have received significant attention due to their quality and affordability.
Foshan Core Deep Medical Apparatus Co., Ltd, according to qcc.com, has a robust production facility and extensive network, allowing them to meet large-scale demands efficiently. They focus on incorporating cutting-edge technology to enhance the user interface and scanning precision of their intraoral scanners.
In conclusion, the intraoral scanner market in China is supported by companies like Shining 3D Tech, Shenzhen Mindray, and Foshan Core Deep Medical, which leverage advanced technology and strategic market positioning to play pivotal roles both domestically and internationally. Their ongoing innovation and competitive pricing continue to make them key players in the global dental equipment industry.
Price Cost Research for Intraoral Scanners manufacturers Companies in China, use temu.com and 1688.com
Conducting price cost research for intraoral scanners from manufacturers in China via platforms like Temu.com and 1688.com can provide valuable insights. Here’s a concise summary:
Temu.com and 1688.com Overview:
– Temu.com: This platform typically caters to global buyers, offering a broad range of products, including medical and dental equipment. Prices may include shipping and be slightly higher due to the international handling.
– 1688.com: A subsidiary of Alibaba, this platform is more focused on the domestic Chinese market, often providing lower prices as it omits international logistics. It’s ideal for bulk purchases and direct manufacturer access.
Steps for Research:
1. Search Keywords: Utilize keywords like “intraoral scanner” (口腔内扫描仪) to find relevant products.
2. Filter Results: Set filters for manufacturer direct sales, price range, and minimum order quantities.
3. Compare Listings: Review multiple listings to gauge average prices and specifications.
Price Range & Notable Manufacturers:
– Price Range: On both platforms, intraoral scanners typically range from $5,000 to $20,000 depending on the brand, features, and included software.
– Top Manufacturers:
– Shenzhen JT Dental: Offers competitive pricing around $6,500 for basic models up to $15,000 for advanced scanners.
– Qingdao Dental: Prices range from $7,000 to $14,000, noted for their customer service and product durability.
– Hangzhou Tevis: Mid-range options from $8,000 to $12,500, popular for their ergonomic designs and easy-to-use software.
Other Considerations:
– Bulk Discounts: Significant savings can be achieved by negotiating directly with manufacturers, especially for bulk orders.
– Shipping and Taxes: Factor in additional costs such as international shipping and import duties when calculating total expenses.
In summary, leveraging Temu.com and 1688.com can reveal competitive pricing for intraoral scanners, with many manufacturers offering high-quality options in the $5,000 to $20,000 range.
Shipping Cost for Intraoral Scanners import from China
Sure, I can provide a general overview of shipping costs for importing intraoral scanners from China, but specific costs will depend on various factors such as shipping method, weight, dimensions, and the destination country.
1. Shipping Methods:
– Air Freight: Quick but more expensive. Cost can range from $5 to $8 per kilogram.
– Sea Freight: Economical for large volumes but slower. Costs could range from $1,000 to $1,500 per container (20-foot).
– Express Delivery: Couriers like DHL, UPS, or FedEx offer fast services at higher rates, typically $30 to $50 per kilogram.
2. Factors Affecting Cost:
– Weight and Volume: Larger and heavier shipments cost more.
– Destination: Distance and accessibility of the destination can impact pricing.
– Custom Duties and Taxes: Different countries have varying import duties for medical equipment.
3. Additional Costs:
– Insurance: Often recommended for expensive equipment like intraoral scanners.
– Handling Fees: Costs for customs clearance and warehousing.
Example Calculation:
Assuming you are shipping a 50 kg package:
– Air Freight: 50 kg * $6/kg = $300
– Sea Freight: If less than container load (LCL), divide container cost by volume.
– Express Delivery: 50 kg * $40/kg = $2,000
Conclusion:
For precise costs, it’s advisable to request quotes from multiple shipping companies and consider all potential fees. Consider the balance between speed and cost to select the most suitable shipping method.
Compare China and Other Intraoral Scanners Markets: Products Quality and Price,Visible and Hidden Costs
When comparing intraoral scanner markets, particularly between China and other global markets, distinct differences in product quality, pricing, and associated costs are noted.
Product Quality:
Chinese intraoral scanners have significantly improved in recent years, offering comparable imaging and scanning speeds to more established Western brands. However, global brands like Align Technology (USA), 3Shape (Denmark), and Carestream (USA) typically maintain an edge in terms of software integration, user interface, and long-term reliability due to their extensive R&D investments and established market experience.
Price:
Chinese intraoral scanners are generally more affordable, often costing 30-50% less than their Western counterparts. This makes them particularly attractive for dental practices looking to minimize initial investment costs. For instance, a mid-range Chinese scanner might cost around $15,000, while a similar device from a Western brand could exceed $30,000.
Visible Costs:
The initial purchase price is more transparent for Chinese products, offering clear upfront savings. Western brands, however, may include additional features such as extended warranties, customer support, and regular software updates within the higher initial cost.
Hidden Costs:
Hidden costs are crucial in the overall assessment. Lower-priced Chinese scanners might lead to higher long-term costs:
1. Maintenance and Repairs: Chinese scanners might need more frequent repairs and have higher downtime.
2. Software Licenses: Some Chinese brands may charge additional fees for software updates or cloud storage, unlike some Western brands that include these in their service contracts.
3. Training and Support: Western brands generally provide superior support and training, which can translate into better utilization and reduced errors, while Chinese brands might offer limited and less comprehensive support.
Summary:
While Chinese intraoral scanners offer a cost-effective alternative with improving quality, Western brands still dominate in reliability, support, and integration. Dental practices must weigh initial savings against potential hidden costs in maintenance, software, and ongoing support when deciding between Chinese and Western intraoral scanners.
Custom Private Labeling and Branding Opportunities with Chinese Intraoral Scanners Manufacturers
Custom private labeling and branding are transformative opportunities for dental practices and businesses looking to differentiate their offerings in the competitive market for intraoral scanners. Partnering with Chinese manufacturers provides distinct advantages in terms of cost-efficiency, advanced technology, and flexibility.
Advantages of Partnering with Chinese Manufacturers:
1. Cost Efficiency: Chinese manufacturers offer competitive pricing due to lower production costs, enabling businesses to achieve higher profit margins or provide more value to customers.
2. Technological Prowess: Many Chinese companies are at the forefront of dental technology, investing significantly in R&D to ensure their products meet global standards.
3. Scalability: Efficient manufacturing processes and large-scale operations facilitate rapid scaling to meet growing demand.
Key Opportunities:
1. Brand Customization: Businesses can collaborate on bespoke designs, colors, and logos to align the scanner’s appearance with their brand identity. This fosters brand recognition and loyalty among dental professionals.
2. Software Integration: Work with manufacturers to tailor software features and user interfaces to meet specific market needs or linguistic preferences, enhancing the user experience.
3. Exclusive Features: Negotiate exclusive rights to certain innovative features or updates which can be marketed as unique selling points to customers.
4. Quality Control: Engage in robust quality assurance processes, ensuring that the product meets both international standards and specific business requirements, thereby bolstering reputation and customer trust.
5. Support Services: Establish branded support and training services, leveraging manufacturer expertise to provide comprehensive after-sales support under your brand name.
Conclusion:
Capitalizing on custom private labeling and branding opportunities with Chinese intraoral scanner manufacturers can significantly boost market presence and competitiveness. Strategic partnerships not only offer cost and technological advantages but also allow for comprehensive customization that aligns perfectly with business goals and customer needs.
Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing Intraoral Scanners
When procuring intraoral scanners for your practice, several key factors can help ensure you make a well-informed purchase:
1. Accuracy and Precision: Ensure the scanner provides high resolution for accurate digital impressions. Verify through clinical studies or independent benchmarks.
2. Ease of Use: Opt for user-friendly interfaces and software to facilitate training and daily operations. Integration capabilities with your existing systems are crucial.
3. Speed and Efficiency: Evaluate the scanning speed, as a faster scanner can improve patient throughput and comfort.
4. Ergonomics: Consider the design’s ergonomics for comfortable handling and reduced physical strain on the operator.
5. Patient Comfort: Soft scanning tips and a small wand size can enhance patient comfort during procedures.
6. Software Capabilities: Advanced software features such as real-time feedback, simulation, and easy workflow integration can enhance productivity and diagnostic capabilities.
7. Data Security: Ensure the scanner offers robust data encryption and compliance with relevant health data protection standards like HIPAA.
8. Cost of Ownership: Analyze the total cost of ownership, including the initial investment, maintenance, software updates, and potential subscription fees.
9. Support and Training: Reliable customer support and comprehensive training are essential for seamless implementation and long-term use.
10. Warranty and Service Plans: Assess the warranty terms and the availability of service plans to minimize downtime.
Additional Considerations:
– Compatibility with Lab Workflows: Check if the intraoral scanner is compatible with your lab’s systems and materials.
– Clinical Applications: Ensure the scanner meets your specific clinical needs, whether for restorative, orthodontic, or implant procedures.
– Feedback from Peers: Consult peer reviews and seek feedback from other professionals who have experience with the model you are considering.
By considering these factors, you can choose an intraoral scanner that meets your clinical needs, enhances patient care, and provides a solid return on investment.
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing Intraoral Scanners in China
Certainly! Here are some FAQs on sourcing and manufacturing intraoral scanners in China:
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing Intraoral Scanners in China
1. Why should I consider sourcing intraoral scanners from China?
China offers competitive pricing, a robust manufacturing ecosystem, and an extensive supply chain. Manufacturers in China also stay up-to-date with the latest technological advancements, ensuring high-quality and innovative products.
2. How do I find reliable manufacturers?
Utilize platforms like Alibaba, Global Sources, and Made-in-China. Attend trade shows like the Canton Fair and Dental South China International Expo. Verify credentials through factory audits, third-party inspections, and by requesting product samples.
3. What certifications should manufacturers have?
Ensure manufacturers comply with ISO 13485 (Medical Device Quality Management Systems) and possess CE and FDA certifications for international market acceptability.
4. How can I verify the quality of intraoral scanners?
Request detailed product specifications and certifications. Conduct third-party inspections and factory audits. Request samples and conduct in-house testing to verify performance and reliability.
5. What is the typical lead time for manufacturing?
Lead times can vary but generally range from 30-60 days after order confirmation. Lead times may be shorter for existing product lines and longer for custom designs or large orders.
6. Can manufacturers provide private labeling or OEM services?
Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and private labeling services, allowing you to brand the scanners under your company’s name.
7. What payment terms are generally accepted?
Common payment terms include Telegraphic Transfer (T/T), Letter of Credit (L/C), and sometimes PayPal for smaller transactions. It’s standard to pay a deposit (30%-50%) upfront and the remainder upon shipment.
8. How do I handle logistics and shipping?
You can opt for sea or air freight depending on urgency and cost considerations. Collaborate with a reputable freight forwarder to handle customs clearance and delivery logistics.
9. Are there potential risks involved?
Common risks include quality inconsistencies, delivery delays, and intellectual property concerns. Mitigate risks with thorough due diligence, clear contracts, and ongoing communication.
By considering these factors, you can effectively source and manufacture intraoral scanners in China, ensuring quality and efficiency.
Contact [email protected] Whatsapp 86 15951276160
